Buying a new engine is costly. But if your car’s engine doesn’t have a cooling system. It can heat up the car. and may deteriorate the car.
Continuously running a car or an automobile can heat up the engine, and reach up to its extreme position beyond your thinking. According to the study, in engine cylinders, the temperature of the burning gases can reach up to 1773.15K – 2273.15K (1500°C – 2000°C). It is more than the temperature and Melting Point of Platinum (1768°C) and Titanium (1668°C), which can oxidize the lubrication oil inside the engine and deposit carbon on the surface.
The amount of heat delivered to the cylinder walls is too high. If the heat is not released from the cylinder. however, it will be the piston, high fuel consumption, pre-ignition, and burning of lubricants, etc.
30% of heat from the engine is convert into mechanical work. 30% of heat is useless and 40% of heat is exhausted through the exhaust fans. The Internal combustion engine cylinder did not generate all heat. It converts the heat into useful power in the crankshaft. a cooling system used to remove the excess heat from the engine cylinder.
An engine cooling system used to maintain the temperature is known as the engine’s cooling system. When there is a car engine gets hot, it removes the heat at a rapid rate. At the beginning of the engine, the engine cooling should be very slow, so that the different working parts can reach their operating temperature in a few time.
Types of cooling systems in Cars
The Two types of cooling systems are used in the engine.
- Air Cooling System
- Water Cooling System
Car Air Cooling System
Air cooling systems (up to 15–20 kW) are used in small engines up to 15–20 kW. In these types of systems, the heat conducted by the outermost parts of the engine is radiated and the air is driven away from the stream. An air-cooled engine is simpler to create than a water-cooled engine because heat is transferred directly from the cylinder and head to the air.
When the automobile is normally driven at sufficient speed to provide sufficient wind speed to transfer heat. The whole cooling system is only the fins on the air-cooled engine. The air-cooled engine has a fan or blower, to improve the airflow in the rear of the wings adequately, with the small or slow movement of air.
As you know the air cooling system is usually used in small automobiles such as scooters, motorcycles, and small cars. It is also provided in some small industrial engines, where the forward speed of the machine gives good velocity to cool the engine.
Air Cooling System Advantages
- It has low manufacturing prices.
- It doesn’t require high maintenance.
- This doesn’t contain liquid coolant, so there will be no problems like leakage and freezing.
- The engine has light in weight because it has no cooling pipe radiator, fan pump, and liquid cooling jacket.
- Installation, assembling, and disassembling of the engine are easy and simple.
Air Cooling System Disadvantages
- The cooling of the engine is non-uniformly.
- In comparison to the water cooling system, it is less efficient.
- This generates aerodynamic noises.
- It can only use for short-sized engines, because of its small capacity for heat wastage.
Car Engine Water Cooling System
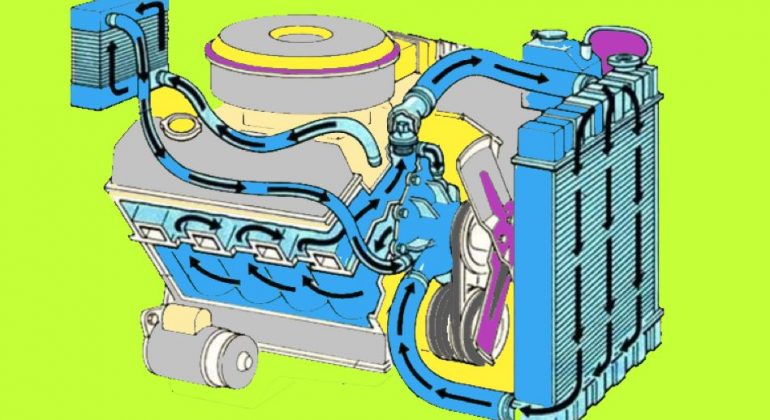
In the water cooling system, water is circulated via the water jacket around each valve seat, valve stems, and combustion chamber. The water-cooled engine block and cylinder head have reciprocating cooling channels. All channels at the top of the cylinder head are converted to a single outlet.
This removes excessive heat generated in the engine and protects it from overheating and keeps the engine at working temperature for efficient and economical work.
The water continuously moves by a centrifugal water pump which is operated by V-belt from the pulley on the engine crankshaft. It drives hot coolant from the engine to the radiator, a form of the heat exchanger. After passing from the radiator, water is poured into the drain and the water is pumped through the cylinder inlet route.
Parts in Water Cooling System
(1) Water Pump:
This is a centrifugal type pump. It is located at the front of the cylinder block and is usually driven by means of a belt. This type of pump consists of the following parts:
- body or casing
- impeller (rotor)
- shaft
- bearings, or bush
- water pump seal
- pulley
The bottom of the radiator is connected to the suction side of the pump. The power is transmitted to the pump spindle from a pulley at the end of the crankshaft. Seals of various designs are incorporated in the pump to prevent loss of coolant from the system.
(2) Radiator:
The main purpose of the radiator is to cool down the water received from the engine. The radiator consist of three parts:
- Upper tank
- Lower tank
- Tube
Hot water from the upper tank, which comes from the engine, flows in the downward direction through the tubes. The heat contained in the hot water is conducted to the copper fins present around the tubes. An overflow pipe, connected to the upper tank, permits excess water or steam to escape. There are three types of radiators:
- Gilled tube radiator- It is the oldest type of radiator, although it is still in use. In this, water flows inside the tubes. Each tube has a large number of annular rings or fins pressed firmly over its outside surface.
- Tubular radiator- The only difference between a gilled tube radiator and a tubular one is that in this case there are no separate fins for individual tubes. The radiator vertical tubes pass through thin fine copper sheets.
- Honeycomb or cellular radiator- The cellular radiator consists of a large number of individual air that is surrounded by water. In this, the blockage of any passage affects only a small part of the cooling surface. However, in the tubular radiator, if one tube becomes clogged, the entire cooling effect is lost.
(3) Fan:
The fan is generally placed on the water pump pulley, although in some engines it is attached directly to the crankshaft. A fan helps to solve two purposes in the cooling system of an engine.
- The fan draws atmospheric air through the radiator and thus increases the efficiency of the radiator in cooling hot water.
- Throws fresh air over the outer surface of the engine, which takes away the heat conducted by the engine parts and thus increases the efficiency of the entire cooling system
(4) Antifreeze Mixture:
In order to prevent the water in the cooling system from freezing, some chemical solutions which are known as anti-freeze solutions are mixed with water. In cold areas, if the engine is kept without this solution for some time, the water may freeze and expand leading to damage in the cylinder block, cylinder head, pipes, and/or radiators. The boiling point of the anti-freeze solution should be as high as that of water. An ideal mixture should easily dissolve in water, be reasonably cheap and should not deposit any foreign matter in the jacket pipes and radiator.
(5) Thermostat Valve:
It is a kind of check valve which opens and closes with the effect of temperature. It is fitted in the water outlet of the engine. During the warm-up period, the thermostat is closed and the water pump circulates the water throughout the cylinder block and cylinder head. When the normal operating temperature is reached, the thermostat valve opens and allows hot water to flow toward the radiator. Standard thermostats are designed to start opening at 70 to 75°C and they fully open at 82°C. High-temperature thermostats, with permanent anti-freeze solutions. start opening at 80 to 90°C and fully open at 92°C. There are three types of thermostats: (a) bellow type, (b) bimetallic type, and (c) pellet type.
- Bellow type valve: Flexible bellows are filled with alcohol or ether. When the bellows are heated, the liquid vaporizes, creating enough pressure to expand the bellows. When the unit is cooled, the gas condenses. The pressure reduces and the bellows collapse to close the valve.
- Bimetallic type valve: This consists of a bimetallic strip. The unequal expansion of two metallic strips causes the valve to open and allows the water to flow into the radiator.
- Pellet type valve: A copper wax pellet expands when heated and contracts when cooled. The pellet is connected to the valve through a piston, such that on the expansion of the pellet, it opens the valve. A coil spring closes the valve when the pellet contracts.
Types of Water Cooling System
- Thermosyphon Cooling System
- Impeller Circulation Cooling System
- Pump Circulation Cooling System
- Pressurized Cooling System
(1) Thermosyphon Water Cooling System:
This system works on the principle that the hot water has a lower density and rises up, and cold water is being heavier than goes down.
The radiator is kept upper the engine, for the easy flow of water. This is how hot water in the water jacket rises and goes over the radiator. Where it passes, cools, and is collected in the bottom tank. In these systems, the rate of supply is too low.
(2) Impeller Circulation Cooling System:
This is an updated version of the thermosyphon cooling system. The main motive of the impeller cooling system is to provide the right regulation, capable of the maximum engine cooling pump efficiency. And it is all the same except that it has a small impeller unit powered by the engine to increase the circulation rate of water.
(3) Pump Circulation Water Cooling System:
This system has the same construction as the thermosyphon cooling system except that it uses a centrifugal pump for circulating water in a water jacket and radiator.
It is a modern system of water cooling in which water is circulated effectively by a cylinder block to the radiator. And come back via a centrifugal pump driven by the engine V-belt.
(4) Pressurized Water Cooling System:
This is an updated version of the pump circulation cooling system. In this, you will get the special radiator cap with a spring-loaded pressure valve and a vacuum valve. When the engine gets heat the cap becomes gas-tight, and water vapor is formed on the cap.
Therefore a raised water boiling point is the system. So that the working temperature of the engine also increases, a higher temperature gives better thermal efficiency.
As the coolant temperature increases, the setpoint of the variable pressure relief valve. Also, increases and the system relief pressure automatically varies with the coolant temperature over a range of pressures whose upper limit is enough greater than the set point of the relief valve in the pressure cap so that the maximum system operating pressure is still finite by the pressure cap.
Water Cooling System Advantages
- The water-cooling system is efficient as compared to the air-cooling system.
- The cylinder, cylinder head, and valve’s uniforming cooling is different from the air cooling system.
- Water-cooled engines have lower fuel consumption than air-cooled engines.
- Water-cooled engines do not require a more frontal area.
- If we install a water cooling system, there is no need for an engine on the front end of the moving automobile.
- The cooling system can be easily located anywhere in the car. In some vehicles, it is at the rear, while in air-cooled engines, this is not possible.
- The engine is less noisy than an air-cooled engine, as it has water for soaking noise.
Water Cooling System Disadvantages
- The water cooling system needs pure water to work properly.
- It totally depends on the supply of water.
- The water pump which supplies the water absorbs a lot of energy.
- In the case of cooling system failure, the engine may suffer severe damage.
- The water coolant system requires regular maintenance, its parts require more maintenance.
- The Water cooling system is expensive because it has many different parts.
- The cost of the water cooling system is quite high.
- The water cooling engine is heavy because it contains lots of water inside. It also has large numbers of parts.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the cooling system of the car prevents the engine from overheating, It also increases the thermal efficiency of the engine. The engine cooling system controls the temperature so that we can easily travel for long hours. Out of the total heat in the engine, 30 to 40% of heat is converted into useful mechanical work. The remaining heat is expelled into the environment through exhausted gas.